Data Cable Explained: Types, Technical Specifications, and Smart Practices
In our connected world, data cables serve as vital lifelines for powering devices and transferring information. With an array of connector types, transfer speeds, and form factors available, selecting the appropriate cable ensures optimal performance, time efficiency, and seamless compatibility across all your tech devices. Here, we will explore what is data cable, discuss common data cable types and their uses, offer Technical Specifications Table, and Provide expert tips for proper usage and maintenance.
Part 1 what is data cable
A data cable is a type of cable used to transfer data between electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and other peripherals. It allows for the transmission of digital information, including files, audio, video, and other types of data. Data cables are essential for connecting devices to each other or to a power source for charging and synchronization.
Part 2 Types of data cable in common
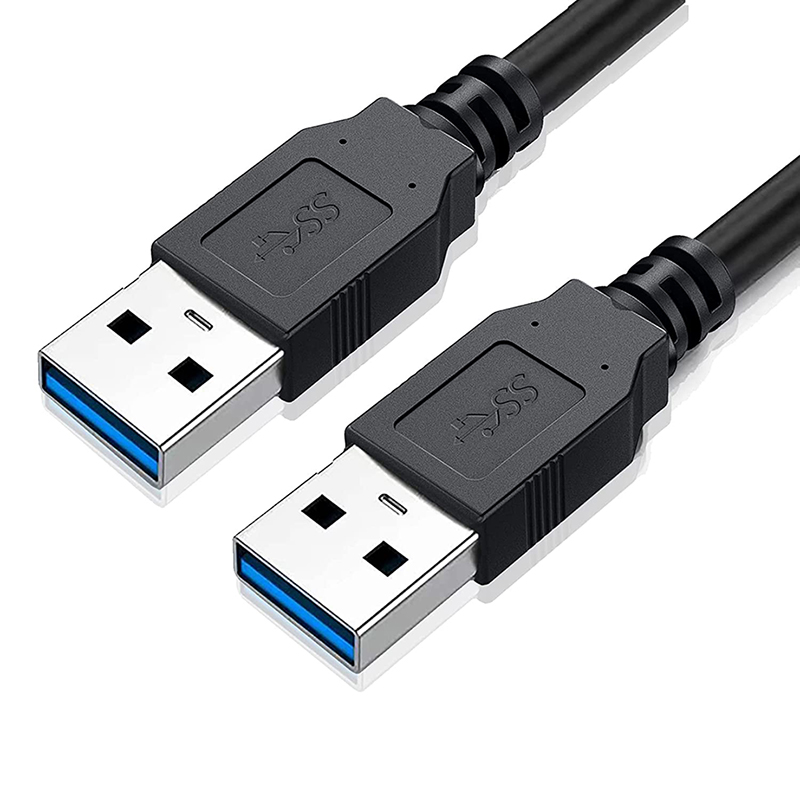
USB-A (Standard USB)
Description:
USB-A is the most common USB connector, recognizable by its flat, rectangular shape. It's widely used for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and flash drives to computers and chargers.
Key Features:
Universal Compatibility: Works with most computers, power adapters, and USB hubs.
Data Transfer: Supports USB 2.0 (480 Mbps) and USB 3.0 (5 Gbps) versions.
Power Delivery: Typically provides 5V/2.4A for charging devices.
Common Uses: Charging smartphones, tablets, and other gadgets. Connecting external hard drives, printers, and USB flash drives.

USB-B (Square USB)
Description:
USB-B features a square-shaped connector with slightly beveled corners. It’s less common than USB-A and is primarily used for printers, scanners, and some audio interfaces.
Key Features:
Sturdy Design: Robust build for devices requiring a secure connection.
Data Transfer: Supports USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 (in larger USB-B 3.0 variants).
Specialized Use: Mostly found in professional and industrial equipment.
Common Uses: Printers, scanners, and older external hard drives. Audio interfaces and MIDI controllers.

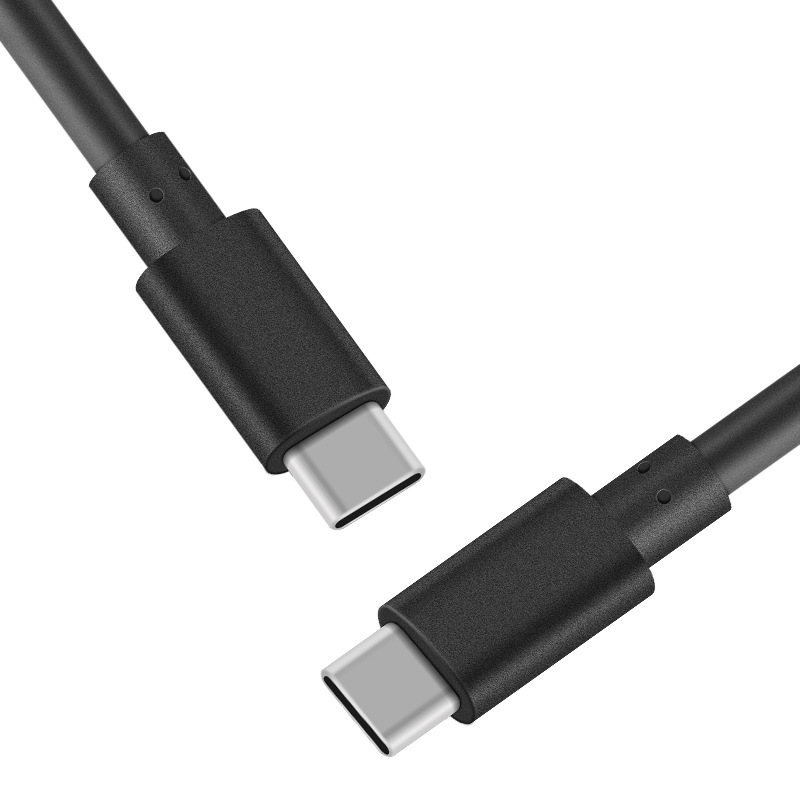
USB-C (Modern USB)
Description:
USB-C is the latest USB standard, featuring a small, reversible oval connector. It’s becoming the universal choice for modern devices due to its high-speed performance and versatility.
Key Features:
Reversible Design: No wrong way to plug it in—saves time and frustration!
SuperSpeed Data Transfer: Supports USB 3.1 (10 Gbps), USB 3.2 (20 Gbps), and Thunderbolt 3 (40 Gbps).
Power Delivery (PD): Can deliver up to 100W for fast charging laptops and smartphones.
Multi-Functionality: Supports video output (DisplayPort/HDMI) and audio.
Common Uses: Latest smartphones (Android, MacBook, tablets). Laptops, monitors, and docking stations.

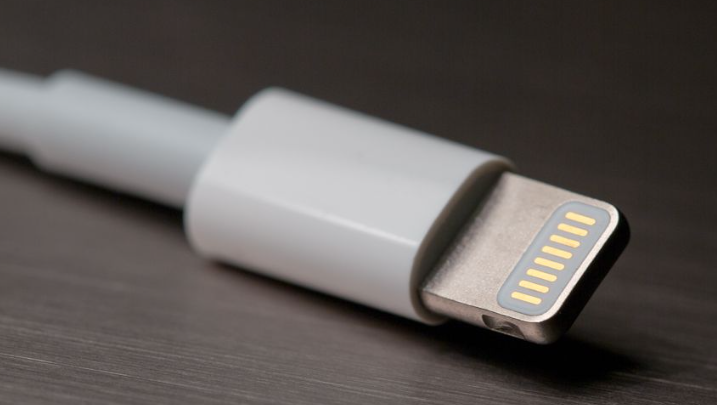
Lightning - Apple's Proprietary Charging & Data Port
Key Features:
Reversible Design (no "wrong way" to plug in)
8-pin compact connector (30% smaller than USB-A)
Supports:
Charging (up to 12W for phones, 35W for iPads)
Data transfer (USB 2.0 speeds - 480Mbps)
Audio output (for wired EarPods)
Device Compatibility:
✔ iPhone 5 - iPhone 14/Plus (pre-USB-C models)
✔ iPad (most models before 2022)
✔ iPod Touch 5th gen+
✔ AirPods (charging case)
✔ MagSafe Battery Pack
Technical Notes: Not waterproof (corrosion risk if wet) MFi Certification Required (Apple's licensing program for 3rd-party cables) Being phased out (EU regulations forcing Apple to adopt USB-C)

Mini USB
Description:
Mini USB is an older, compact USB connector that was widely used in early 2000s portable electronics before being replaced by Micro USB and USB-C.
Key Features:
Smaller than standard USB-A but bulkier than Micro USB
USB 2.0 speeds (480 Mbps max)
5-pin design with trapezoidal shape
Less durable (~5,000 insertions) compared to Micro USB
Common Uses: Early digital cameras Older MP3 players (like early iPods) Some GPS devices and portable hard drives
Why It's Obsolete: Phased out due to durability issues Micro USB became the new standard (smaller & more robust) Now rarely seen except in very old electronics

Micro USB
Description:
Micro USB is a compact USB connector commonly used for charging and data transfer in older smartphones, tablets, and small electronic devices.
Key Features:
Small & Slim: Smaller than Mini USB, designed for thinner devices.
Durability: Rated for ~10,000 insertions (more durable than Mini USB).
Universal Charging: Became the standard for Android devices (pre-USB-C era).
Common Uses: Older Android phones, power banks, Bluetooth speakers. Budget devices and some IoT gadgets still use it today.
Note: Non-reversible (must be inserted correctly). Slower than USB-C (typically USB 2.0 speeds).

Part 3 Technical Specifications Table for Data Cables
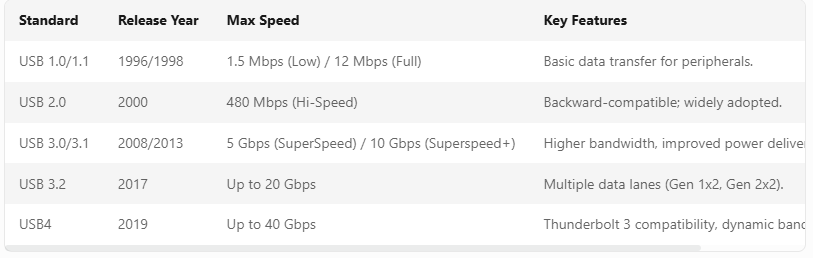
Part 4 Smart Practices for Data Cable Care & Optimization
1. Proper Handling Techniques
Insert/Remove Correctly: Always grip the connector head (not the cable) when plugging/unplugging
Avoid Tension: Never wrap cables tightly around devices or chargers - use loose loops instead
2. Charging Best Practices
Match Power Ratings: Use cables rated for your device's fast-charging requirements
Unplug When Not in Use: Prolongs both cable and device battery lifespan
3. Cleaning & Maintenance
Regular Inspection: Check for fraying, exposed wires, or loose connections monthly
Storage Solutions: Use velcro ties or cable organizers to prevent tangles

