Battery Cable: Everything you need to know
Battery cable assemblies power our modern world as critical yet often overlooked components. These essential systems enable efficient energy transfer from batteries to electrical devices across countless applications and industries. This guide examines battery cable assembly types, key uses, industry applications, emerging trends, and vital considerations for optimal performance.
What are Battery Cable Assemblies?
A battery cable assembly serves as the essential power bridge between a battery and electrical systems. These engineered components—comprising precisely designed cables, terminals, and connectors—form the backbone of energy distribution in countless applications.
In automotive systems, they deliver high-current power to starters, alternators, and vehicle electronics. Industrial applications rely on their robust construction to operate heavy machinery, while renewable energy installations depend on their efficiency for solar/wind power transmission.
Key features of Battery Cable Assemblies
Connectors
There are numerous connector types used for battery connections with the most common being the standard battery terminal that goes over a lead post and the ring lug terminal. They come in straight and right-angle configurations to fit various wire gauges. They are typically made of copper and come in plated and bare copper variations. The connectors include JST MOLEX JAE RCA and other type.
Length
When determining the appropriate length of automotive wire or cable, it's essential to account for voltage drop—the gradual loss of voltage along the conductor. Since electrical resistance increases with wire length, excessive length can lead to an unsafe voltage drop, potentially compromising system performance. Therefore, wires should be kept as short as possible to maintain optimal voltage levels.
Wire Gauge Selection
Battery cables are available in various wire gauges, allowing electricians to select the appropriate size based on power requirements. Larger cables have a higher current-carrying capacity, but the maximum safe current depends on factors such as the cable's intended application, installation environment, and ambient temperature.
Different Types of Battery Cable Assemblies
Copper-Based Battery Cables
Sectors/Industries Served: Automotive, heavy machinery, marine systems.
Key Strengths: Renowned for exceptional electrical conductivity and reliability in power transmission. Offers robust corrosion resistance and long-term durability.
Design Considerations: Higher density and cost compared to alternative materials may limit flexibility in weight-sensitive or budget-constrained scenarios.
Aluminum Alloy Battery Cables
Sectors/Industries Served: Industrial equipment, renewable energy grids (e.g., solar/wind installations).
Key Strengths: Lightweight construction with balanced conductivity and cost efficiency. Protective coatings enhance corrosion resistance for outdoor environments.
Design Considerations: Requires larger cross-sectional areas than copper to achieve equivalent current-carrying capacity.
Hybrid-Conductor Battery Cables
Sectors/Industries Served: Applications demanding cost-performance optimization (e.g., hybrid vehicles, portable power systems).
Key Strengths: Integrates copper cores for superior conductivity with aluminum exteriors to reduce overall weight and material costs.
Design Considerations: Requires precise engineering to ensure seamless integration of dissimilar materials and maintain structural integrity.
Custom Engineered Battery Cables
Sectors/Industries Served: Niche applications with unique technical requirements (e.g., aerospace, hazardous environments).
Key Strengths: Fully customizable material compositions, insulation types, and connector designs to meet precise specifications.
Design Considerations: Demands in-depth analysis of operational conditions and potential trade-offs between performance, safety, and budget.
Application of Battery cable used
Battery cables serve as the fundamental power connection between batteries and starters across multiple transportation sectors. These robust cables are specifically engineered for demanding applications in:
Automotive & Transportation:
Heavy-duty trucks and buses requiring high-current delivery
Recreational vehicles (RVs) with complex power systems
Agricultural and construction equipment like tractors
Marine vessels where corrosion resistance is critical
Technical Advantages:
Optimized Routing: Performs best in straight-line installations with minimal 90-degree bends
Cost-Effective Solution: More economical than specialized wiring (e.g., welding cable)
Voltage Compatibility: Standard 60V DC rating suitable for most vehicle electrical systems
Configuration Flexibility: Available in various gauge sizes to match specific power requirements
Performance Characteristics:
The cable's superior durability stems from:
Heavy-gauge copper conductors for maximum current flow
Oil-resistant insulation materials
Engineered to withstand vibration and mechanical stress
Temperature-tolerant construction for engine compartment environments
Selection Considerations:
When choosing battery cables, key factors include:
Current carrying capacity requirements
Environmental exposure conditions
Connection point distances
Flexibility needs for installation routing
Some parts of battery cable we made
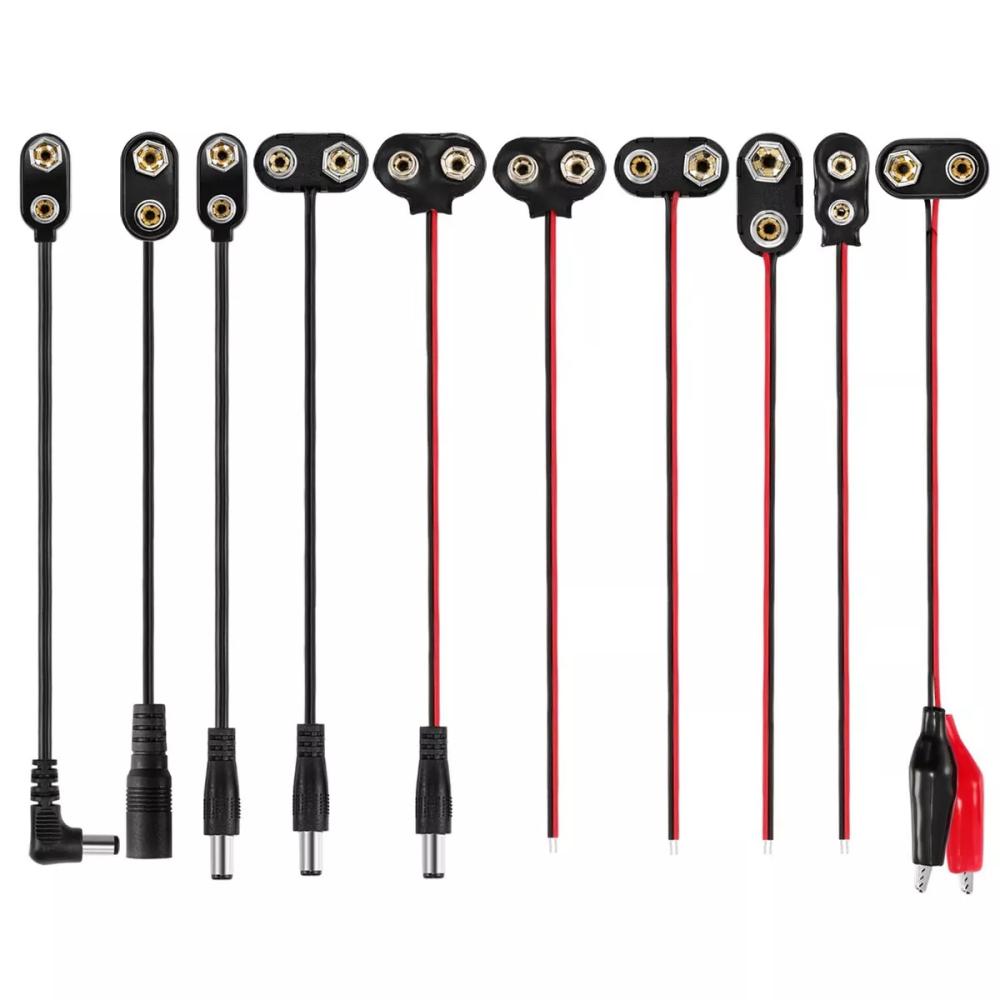

9V battery clip connector
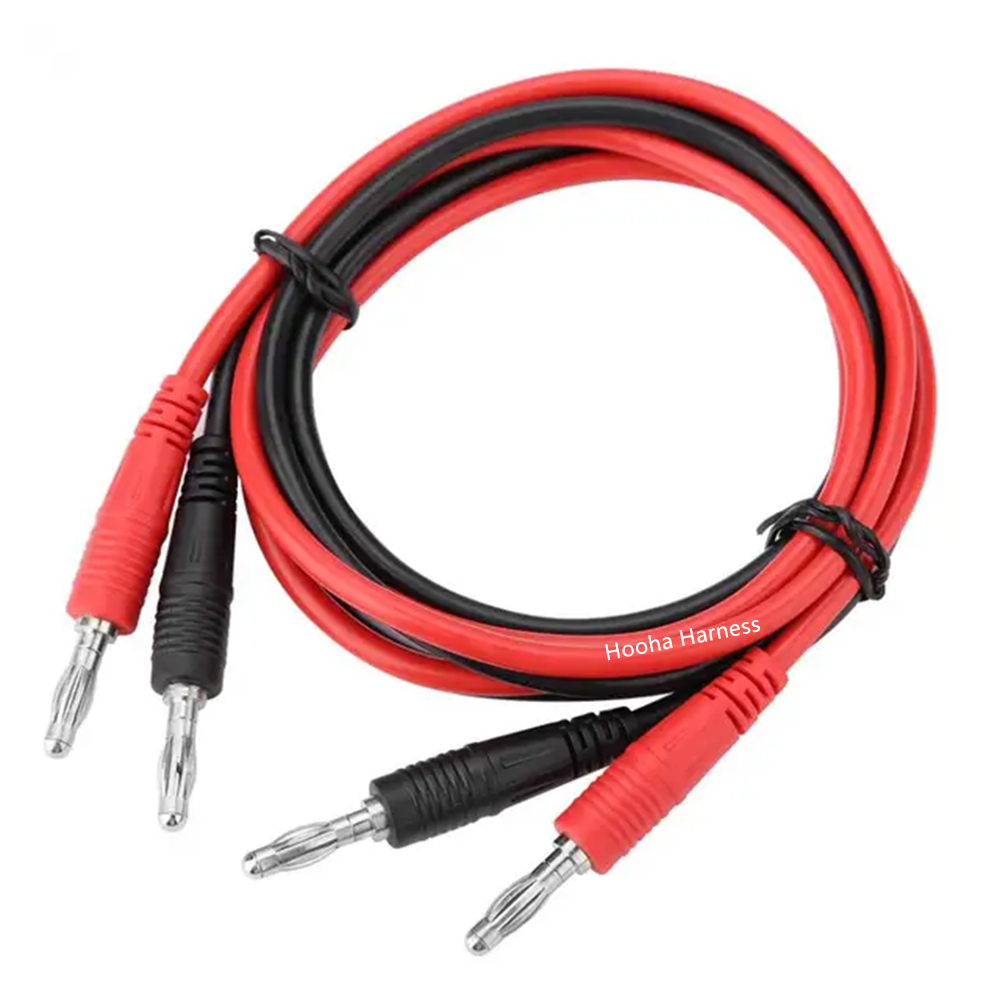

Banana Plug test cable
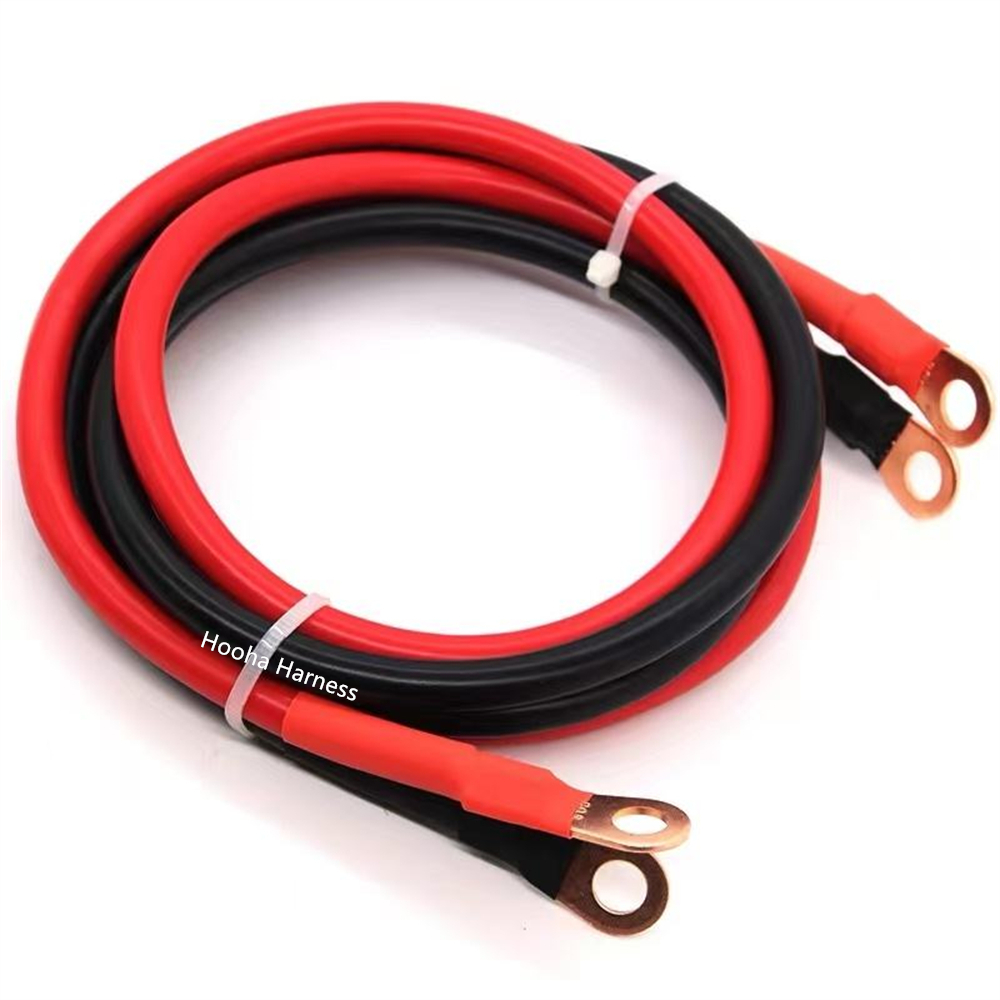

battery pack jumper
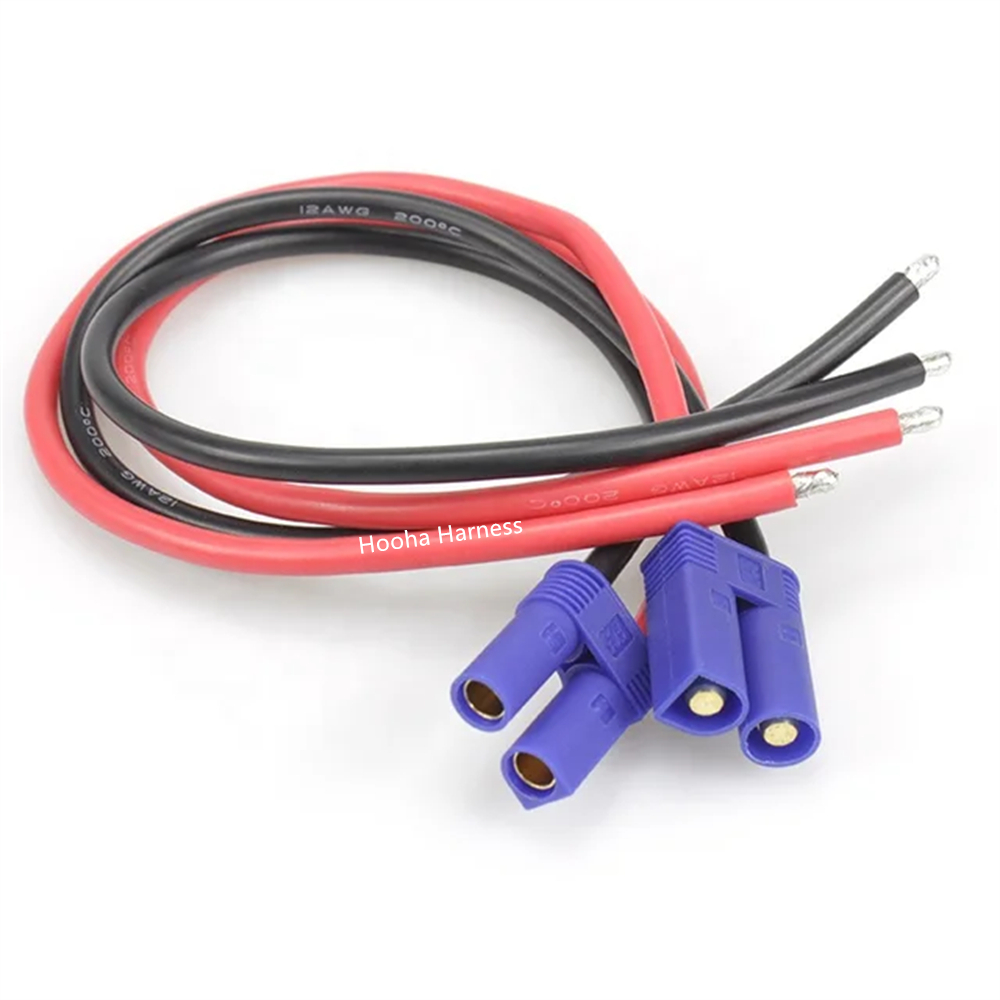

EC5 battery cable
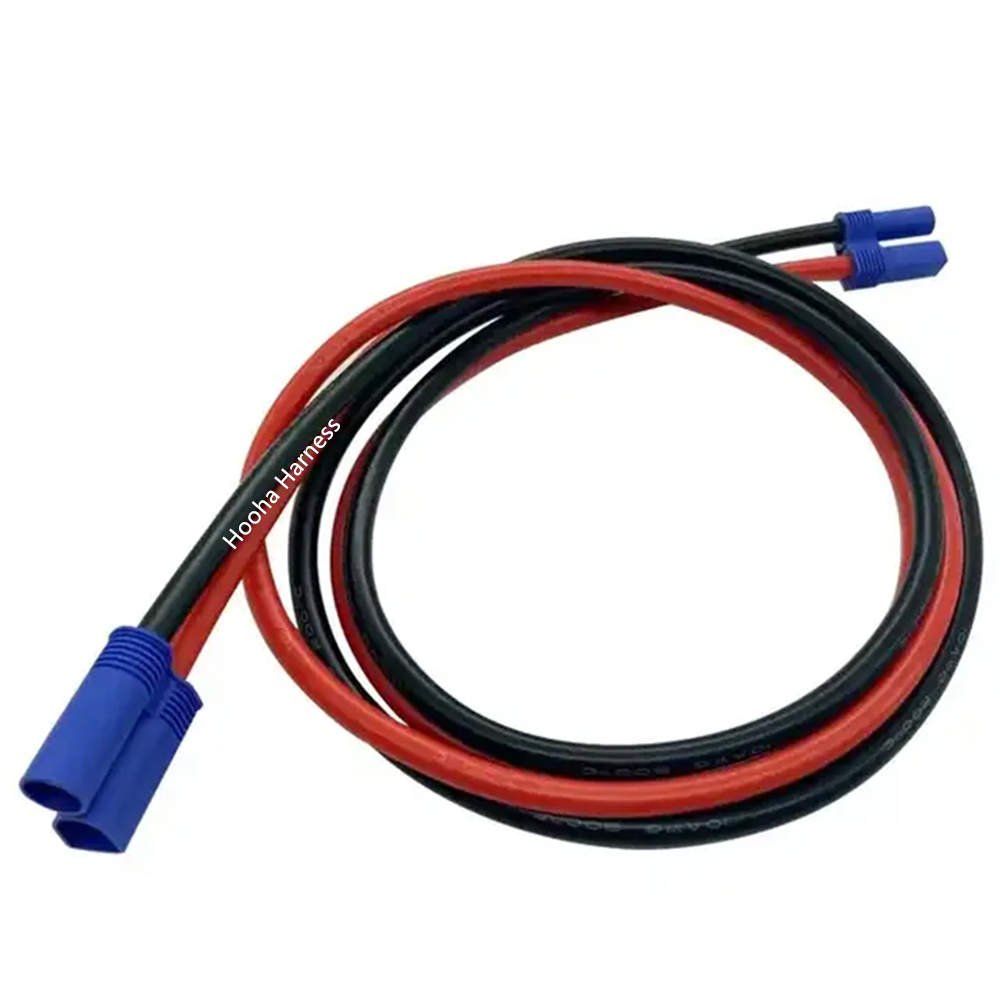

ec5 battery connector
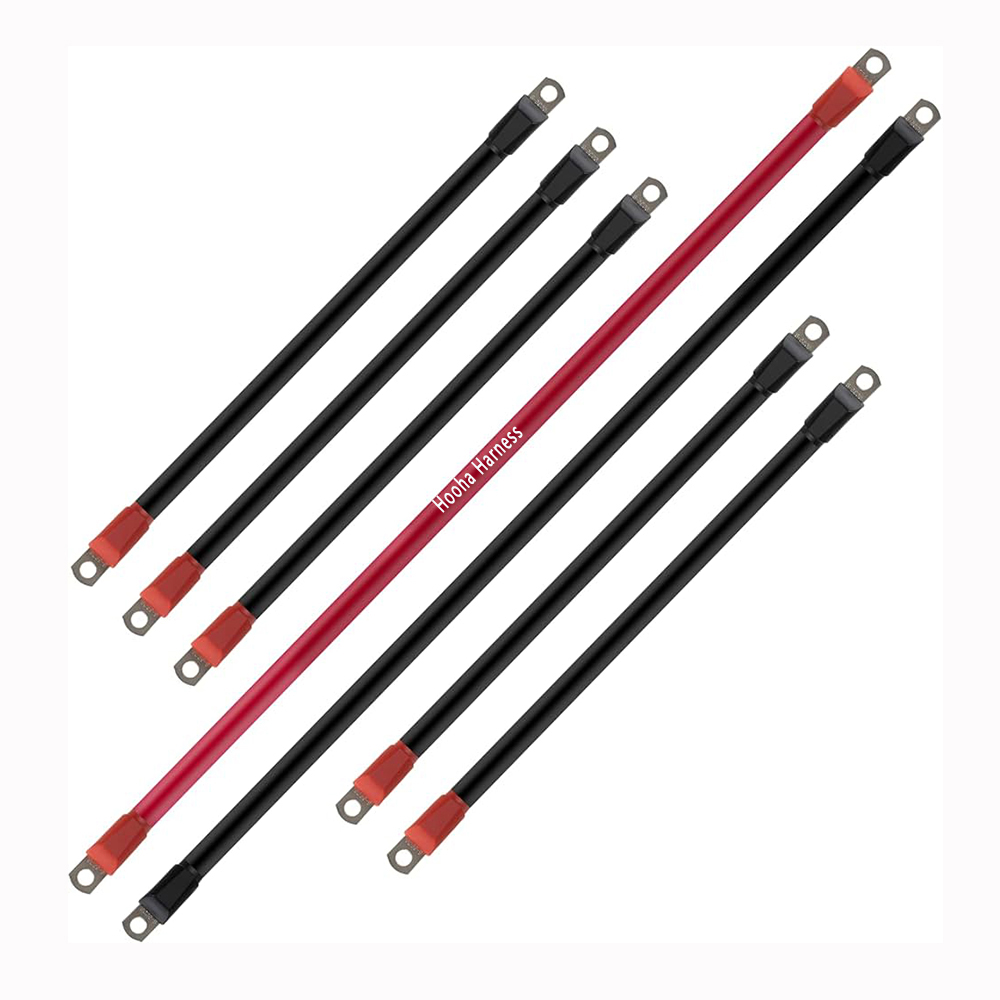

golf cart cables
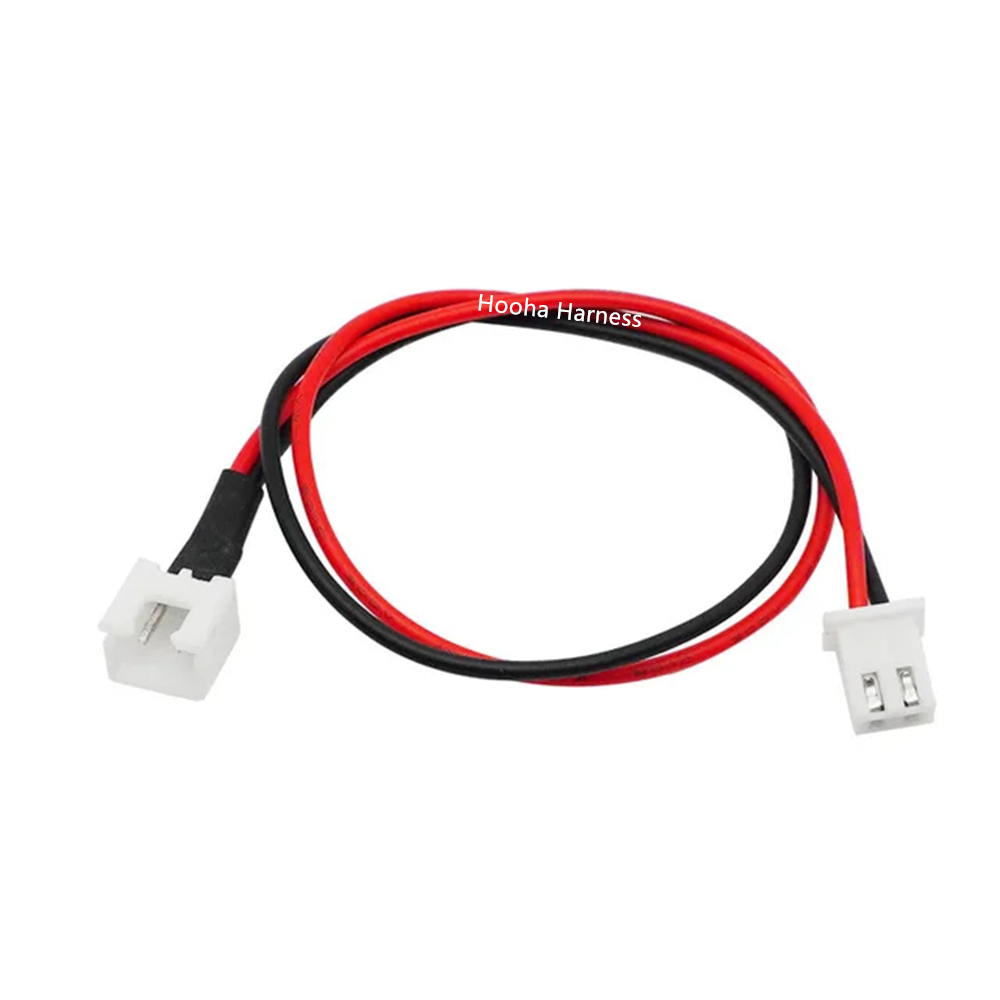

JST PH 2P battery cable
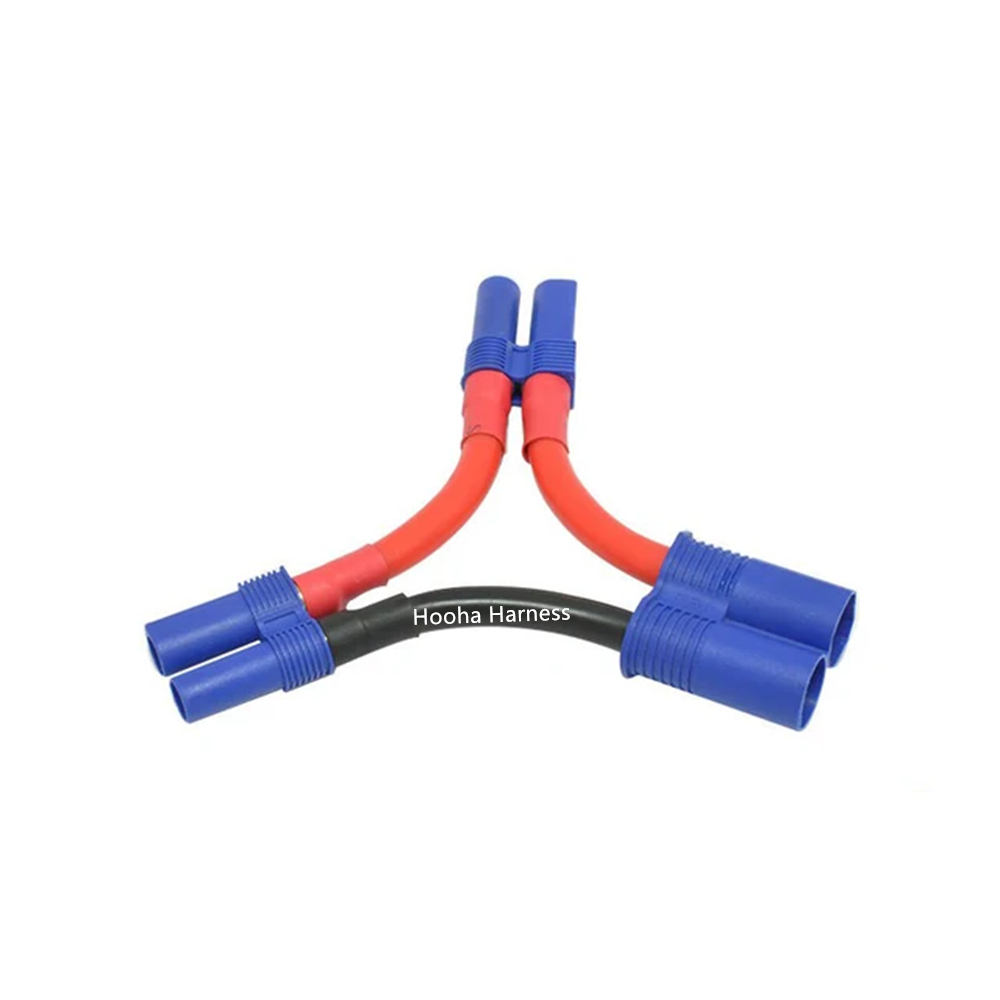

RC battery cable
sae to sae cable
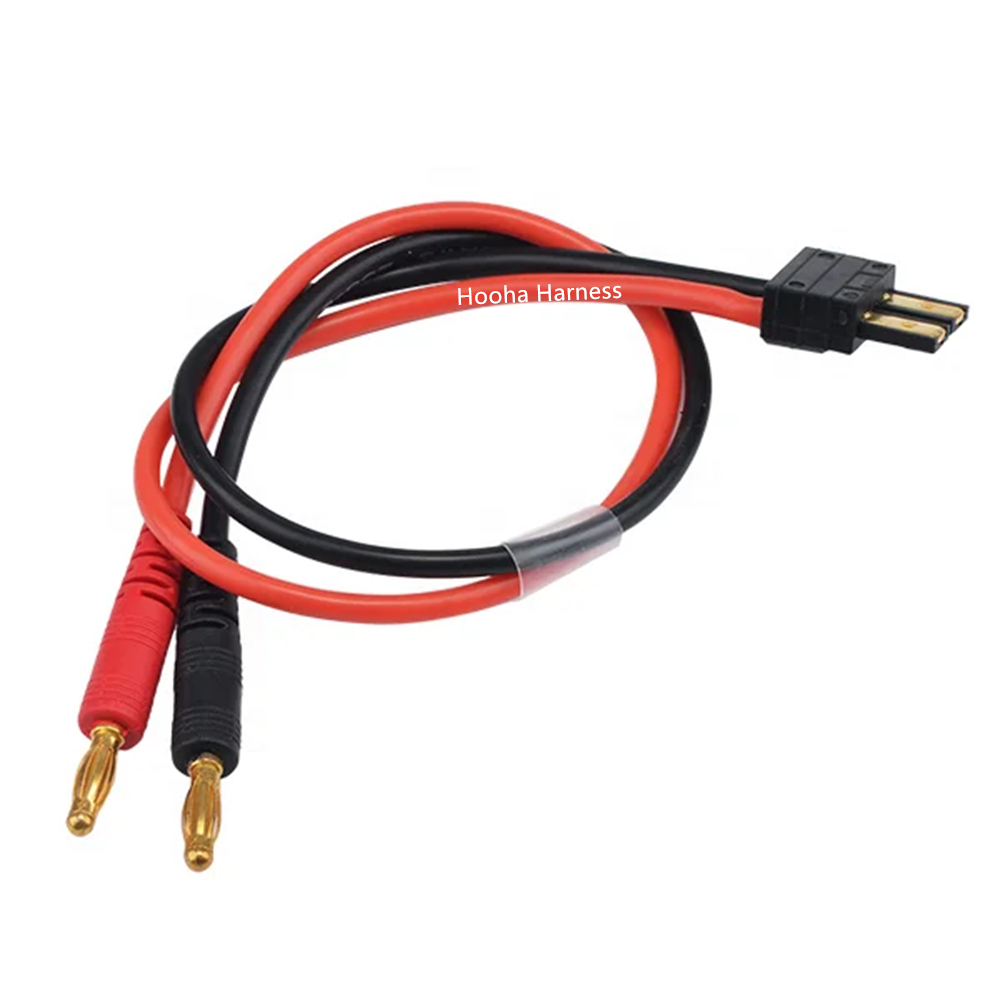

TRX Charge Cable
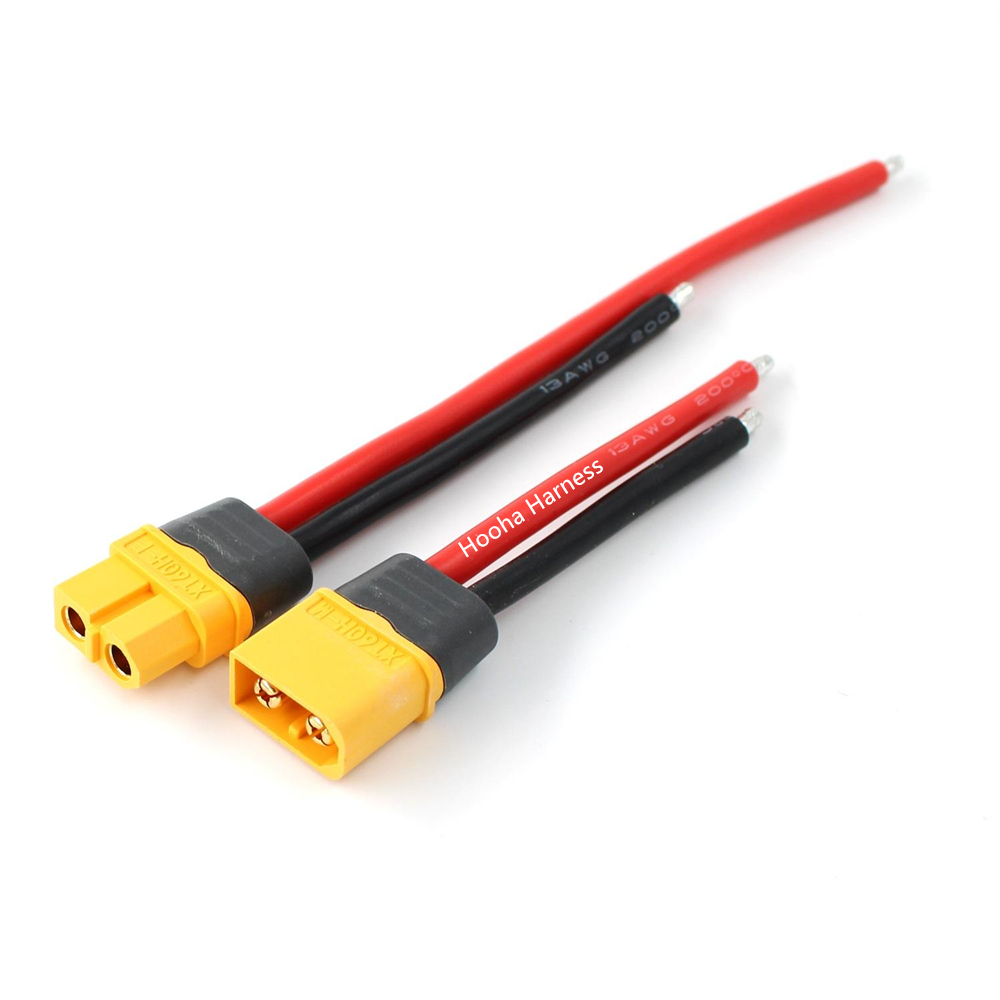

XT60 connector
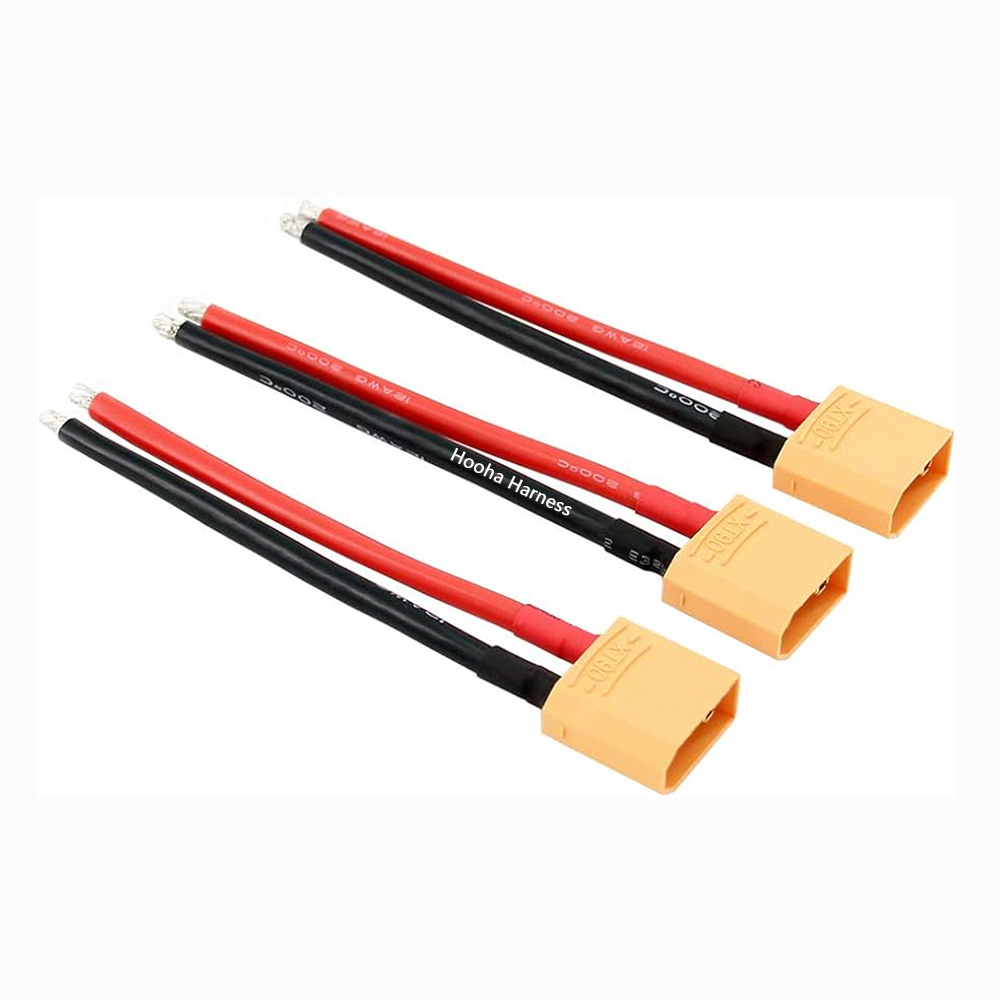

XT90 12AWG wire
